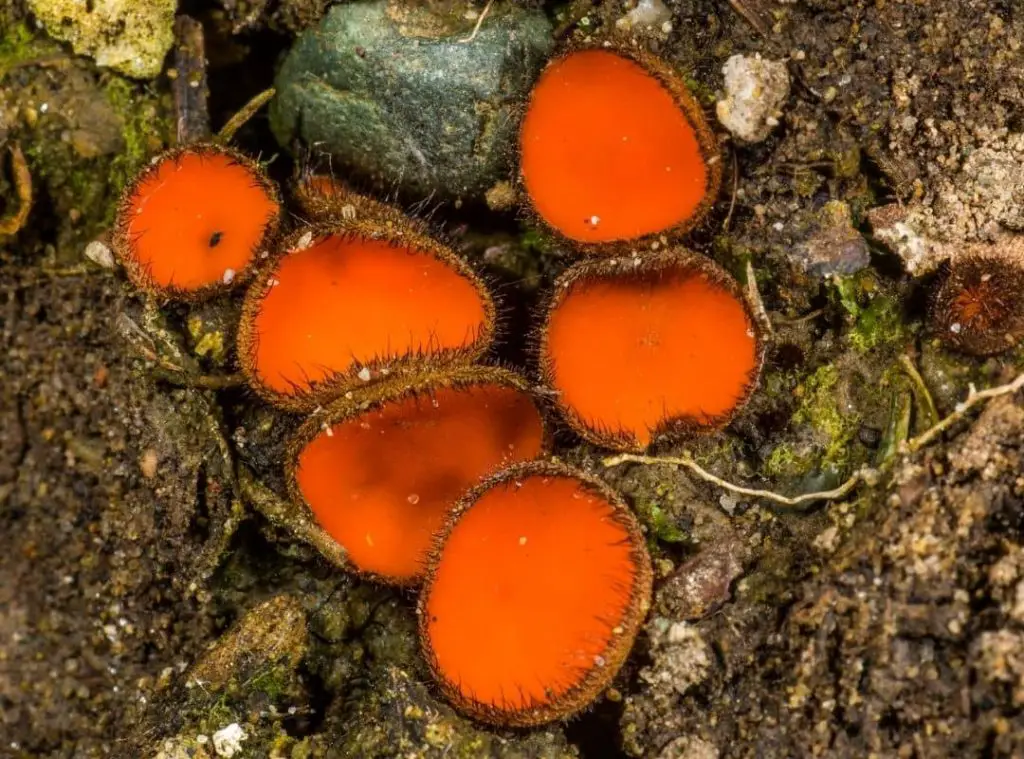
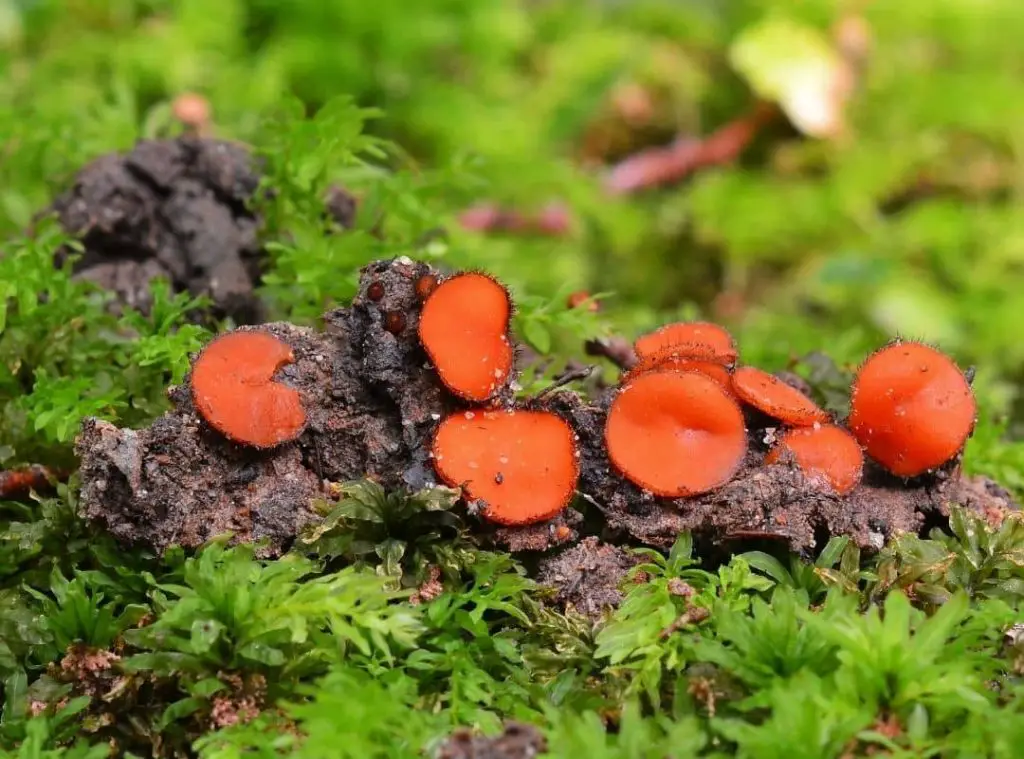
Scutellinia scutellata is a saprophytic fungus called Eyelash cup, Common eyelash, or Molly eye-winker. It has a disk-shaped and red-colored fruit body. Scutellinia scutellata is small in size. The fruit body is covered by hair. Carl Linnaeus named this mushroom as Species Plantarum. But in 1887, Jean Emil Lambotte changed its name to Scutellinia scutellata.

How can you identify the Scutellinia scutellata?
Contents
- 1 How can you identify the Scutellinia scutellata?
- 2 What size is Scutellinia scutellata?
- 3 Where can we find Scutellinia scutellata?
- 4 When do Scutellinia scutellata grow?
- 5 Is Scutellinia scutellata poisonous?
- 6 Can I eat Scutellinia scutellata ?
- 7 Scutellinia scutellata recipes
- 8 Where can I buy Scutellinia scutellata?
- 9 Symptoms of Scutellinia scutellata poisoning
- 10 Scutellinia scutellata look-alikes
- 11 Conclusion
It is a disk-shaped stalkless mushroom. The color of the disk varies from deep red to orange. The disk is about 4mm in diameter. The disk is irregularly shaped and flat in appearance. The spore-bearing surface is shiny and the disk-shaped fruit body is covered by dark-colored hair. The hair grows up to about one centimeter and the hair is stiff. This hair is the characteristic feature to identify Scutellinia scutellata. The hairs of this mushroom are called “eyelashes”.
It has thin, red-colored flesh and this mushroom is stemless. They grow as clusters or small groups. Cheilymenia sp. Is similar in physical appearance but they are two different species. This mushroom has an orange-colored flat fruit body. Sometimes this mushroom can be observed on cow pats or on other animal dung.
Cap
The cap is flat and disk-shaped. It gets its common name ‘Common Eyelash’ due to the appearance of the cap. The cap has a color varying from deep red to orange and the upper surface is shiny. The cap is about 3 to 5 mm in diameter. The outer surface is infertile.
Gills
It has no gills. The spores of Scutellinia scutellata are produced in the inner surface and the inner surface is shiny. The asci bear the spores. There are eight spores in an ascus.
Stem
It is stemless. It is attached to the substrate using threads called mycelial threads.
Spore print
The spore print of Scutellinia scutellata is White and the spores are called ascospores.
Microscopic features
Fruiting body: This is about 300 x 25 µm
Spores: It is an ascomycetes fungus, therefore spores are ascospores. These spores are elliptical shaped. The spores are about 17-23 x 10.5-14 µm in size and white colored. When in the immature stage, spores are smooth. The ascospores consist of oil droplets.
Marginal hairs: These hairs are called ‘Eyelashes’. The hairs are about 360-1600 x 20-50 µm in size.
What size is Scutellinia scutellata?
It is about 3-20mm in width.
Where can we find Scutellinia scutellata?
They grow on damp soil or they can be grown on well-decayed woods or bark and moisture is another factor in the growth of scutellinia. These fungi can become stronger, therefore this can spread in a wide range. They are most common in Ireland and Britain. Also, this fungus spread in South America, North America, Australia, Europe and Asia as well.
When do Scutellinia scutellata grow?
They grow from June to November. (late spring to late autumn season)

Is Scutellinia scutellata poisonous?
There is no evidence or studies related to their toxicity.
Can I eat Scutellinia scutellata ?
They are inedible due to the lack of a unique smell or taste. But Scutellinia scutellata is rich with carotenoids. Not only are carotenoids, but they also consist of small amounts of xanthophyll.
Scutellinia scutellata recipes
They are inedible. According to several studies consuming raw mushrooms or consuming after boiling is not recommended.
Where can I buy Scutellinia scutellata?
You can find them in damp places. Because this fungus likes to grow in an environment with moisture and on decaying woods, wet leaves as well as ashes. According to some studies, Scutellinia scutellata is not an economically important fungus.
Symptoms of Scutellinia scutellata poisoning
According to some studies they are inedible.
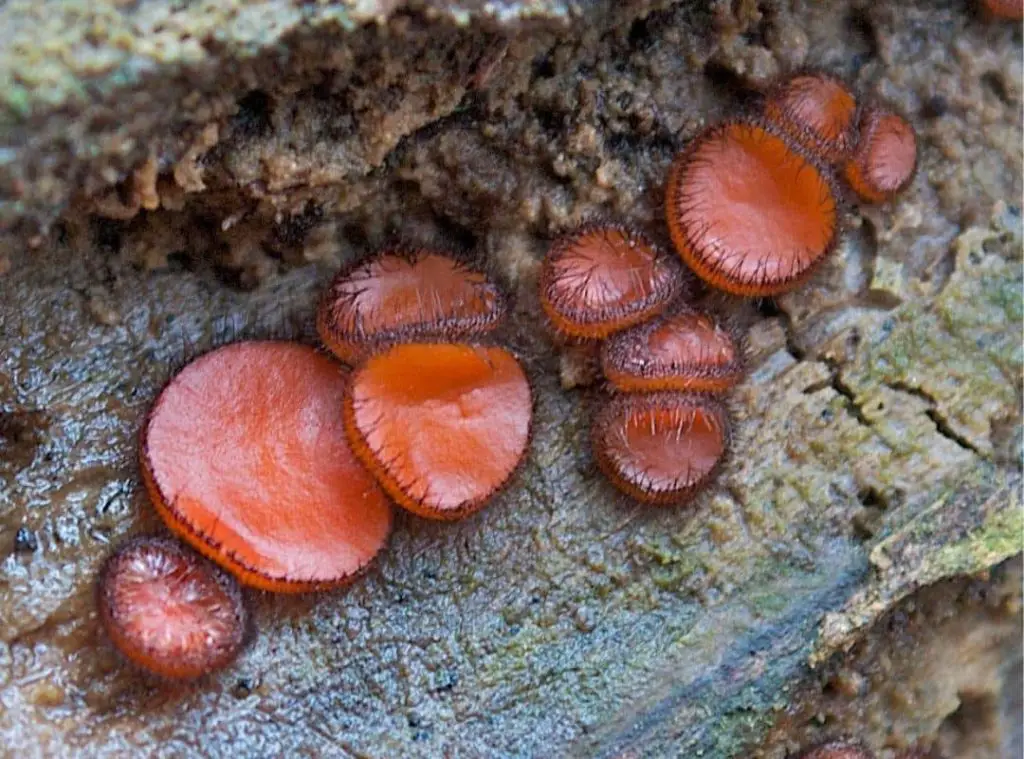

Scutellinia scutellata look-alikes
Most lookalike species can distinguish using the following factors:
Presence of hair, hair size, spore print, spore shape, fruit body size and color. All of these features are microscopic. Sarcoscypha austriaca is one of the similar species to Scutellinia scutellata. It is also named the ‘Scarlet Elf Cup’. This fungus has a bright red cup-like Scutellinia scutellata but the size is larger than scutellinia. Both species can be differentiated by the marginal hairs. Sarcoscypha has no hairs on the margins.
Scutellinia umbrorum is also a bright red-colored, disk-shaped fungus. This fungus can be mistakenly identified as Scutellinia scutellata. Scutellinia umbrorum margin consists of hairs. These hairs are shorter than S. scutellata. The spores and fruit bodies of S. umbrorum are larger than S. scutellata.
The above two species distinguish using these physical differences. Sometimes you need a microscope to observe these features. S. umbrorum is an inedible mushroom. Scutellinia erinaceus is another S. scutellata lookalike species. This fungus is named ‘Orange Eyelash cup’. S. erinaceus is a yellowish or pale orange-colored saprobic fungus. The margin hairs are long and brown.
Grow as clusters and grow on decaying woods. These fungi are also inedible as S. scutellata. Melastiza chateri also looks like S. scutellata. This has dull orange, smooth disk and margins consist of short hairs. Cheilymenia crucipila is orange colored cup fungus. This has branched shorter marginal hairs and hairs also transparent. Usually observed on animal dung.
Conclusion
The shape of this mushroom is similar to an eye with eyelashes. Therefore it is named Common Eyelash. This is mainly a red-colored, disk-shaped fungus. The margin is covered with pointed, dark brown colored marginal hairs. Scutellinia scutellata is a moist-loving fungus that uses decayed wood or barks or soil to grow. These mushrooms are distributed mainly in Ireland and Britain and the season is late spring to late autumn. Scutellinia scutellata is a stemless fungus that grows in small groups or clusters. This is an inedible mushroom with no unique taste or smell.
There are no records of toxicity of S. scutellata. Not only raw mushrooms but also boiled mushrooms of S. scutellata are not suitable to consume. Scutellinia umbrorum, Cheilymenia crucipila, Sarcoscypha austriaca, Scutellinia erinaceus and Melastiza chateri are some Scutellinia scutellata looksalikes. Most of them can’t distinguish suddenly by the naked eye. These mushrooms have few morphological differences, which can distinguish the species separately such as the color of the fruiting body, marginal hair color and length, etc. These mushrooms are common in damp places and there are no records as illegal mushrooms.
Read Next : Coral Mushroom Edible | With Delicious Recepies |